The automation wave: which roles change first and what replaces them

The rapid advancement of technology is ushering in a significant automation wave that is transforming industries worldwide. Businesses are increasingly adopting automated solutions, which is prompting a shift in employment roles and the nature of work itself. Understanding which roles are most affected and what technologies or systems replace them is crucial for both workers and employers preparing for this transition.
Early adopters of automation: roles most affected
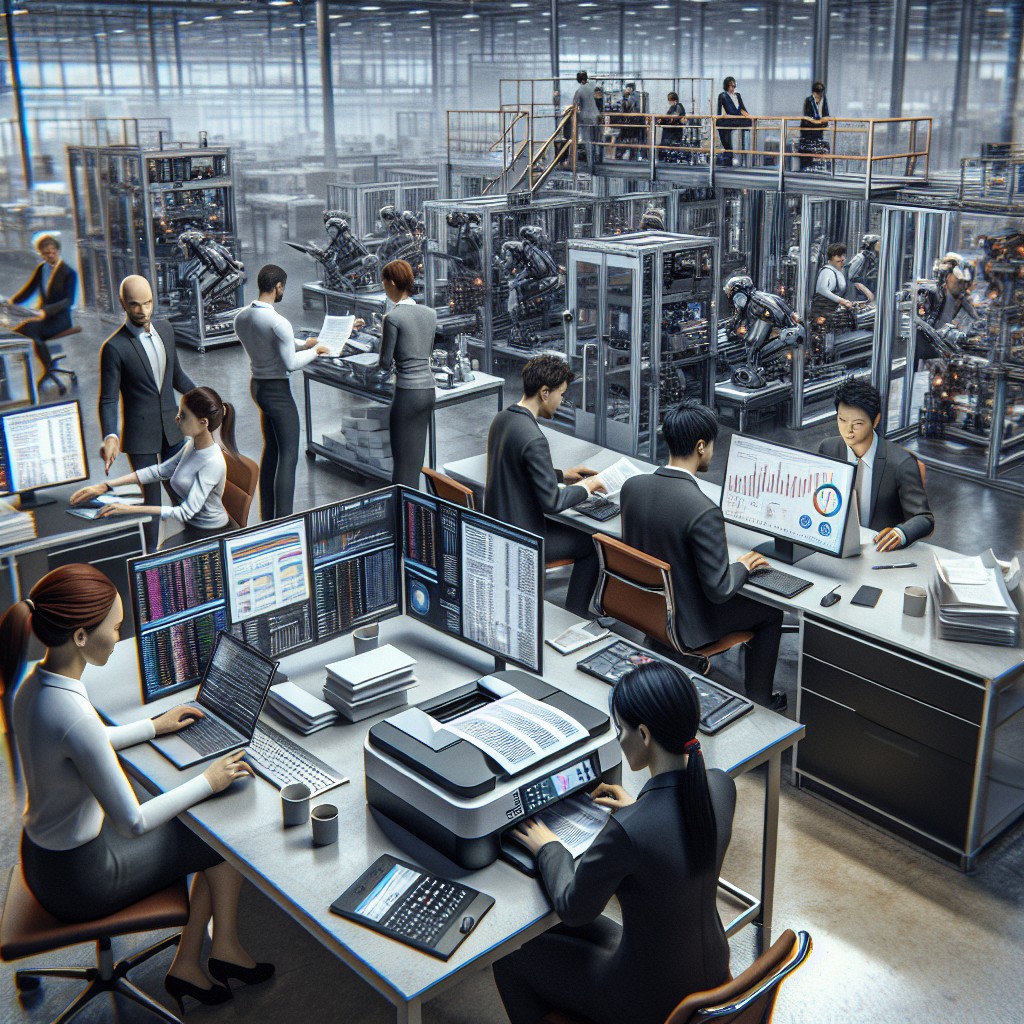
The initial phase of the automation wave predominantly impacts jobs involving repetitive, routine tasks. Manufacturing assembly line workers, data entry clerks, and certain administrative positions are examples where machines and software can perform faster and with fewer errors. These jobs often involve structured processes that are easily programmable, making them prime candidates for early automation implementation.
Technologies driving the automation wave
Key technologies catalyzing the automation wave include robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning algorithms. Robotics have revolutionized production lines by handling complex physical tasks, while AI powers decision-making systems that can analyze vast datasets to optimize operations. Furthermore, process automation software streamlines administrative workflows, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing overall efficiency.
The impact on service and knowledge industries
While manufacturing roles experience immediate transformation, service and knowledge sectors are also undergoing considerable shifts due to the automation wave. Customer service roles are increasingly supplemented by AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants that can address common inquiries without human involvement. In finance and legal industries, automation is used to expedite document analysis and routine tasks, allowing professionals to focus on more strategic functions.
New roles emerging from automation
The automation wave not only replaces certain positions but also creates new roles centered around managing and optimizing automated systems. Positions such as automation specialists, AI trainers, and robotics maintenance technicians are gaining prominence. These emerging jobs require a blend of technical expertise and problem-solving skills, indicating a shift in demand towards more skilled labor as routine roles diminish.
Challenges and considerations for workforce adaptation
As the automation wave progresses, workforce adaptation remains a significant challenge. Workers displaced from routine roles may need retraining to transition into new positions created by automation technology. Policymakers and companies must collaborate to develop educational programs and reskilling initiatives that prepare employees for the evolving job market. Ensuring equitable transition measures is essential to mitigate social and economic disruptions caused by this technological shift.
Conclusion
The ongoing automation wave is reshaping the employment landscape, first targeting roles with repetitive tasks and gradually affecting a broader range of industries. While automation replaces some jobs, it simultaneously generates new opportunities requiring advanced skills. Navigating this transition will depend on effective workforce development strategies and proactive adaptation by both individuals and organizations, highlighting the need for continuous learning in a technology-driven economy.
Frequently Asked Questions about automation wave
Which roles are most vulnerable during the automation wave?
Roles involving repetitive and routine tasks, such as manufacturing assembly workers and data entry clerks, are most susceptible to automation replacement in the early stages of the automation wave.
What technologies are behind the current automation wave?
Robotics, artificial intelligence, and process automation software are key technologies driving the current automation wave, enabling machines to perform tasks traditionally done by humans.
How does the automation wave affect service industry jobs?
The automation wave is introducing AI-driven tools such as chatbots in customer service, reducing reliance on human agents for routine inquiries but allowing employees to focus on complex interactions.
Are new jobs created as a result of the automation wave?
Yes, the automation wave creates new positions like automation specialists and AI trainers, which require technical skills to manage and improve automated systems.
What measures can help workers adapt to changes caused by the automation wave?
Reskilling programs, education in emerging technologies, and proactive workforce development initiatives are crucial to help workers transition during the automation wave.